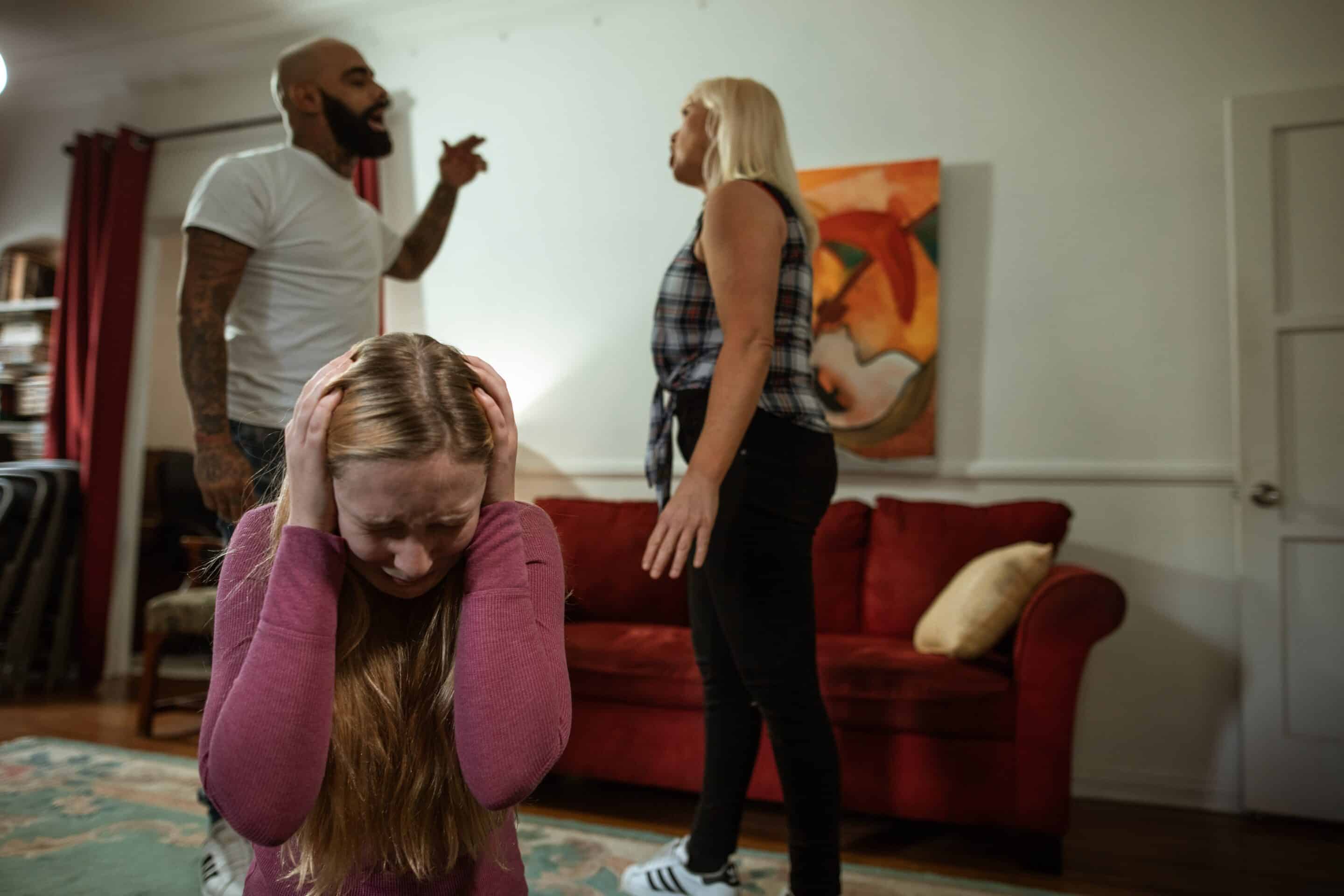
Childhood trauma can seriously impact a person’s life in ways that can last a long time. One aspect where these effects can be especially noticeable is in how they relate to addiction. Studies have revealed a clear link between childhood trauma and a higher likelihood of developing problems with substance abuse as one grows older.
The Impact of Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma can take many forms, including physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, neglect, or witnessing violence at home. These experiences can have a long-term impact on a child’s developing brain, disrupting normal emotional and cognitive development and leading to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It can also increase the likelihood of engaging in risky behaviors, such as substance abuse, to cope with the pain and distress associated with the trauma.
The Self-Medication Hypothesis
The self-medication hypothesis suggests that individuals who have experienced trauma may turn to substances to numb the emotional pain or distressing memories. Drugs and alcohol can temporarily relieve the intense emotions associated with trauma, creating a cycle of self-medication that can quickly spiral into addiction. The desire to escape the painful memories or feelings associated with trauma can make individuals more susceptible to substance abuse.
Altered Brain Reward System
Furthermore, childhood trauma can alter the brain’s reward system, which plays a crucial role in addiction. The chronic stress and emotional dysregulation experienced during childhood trauma can lead to changes in the brain’s neurotransmitter systems, particularly those involving dopamine, a chemical messenger associated with pleasure and reward. These changes can make individuals more susceptible to the rewarding effects of drugs and alcohol, increasing the likelihood of developing addiction.
Coping Mechanisms and Maladaptive Behaviors
Childhood trauma can also impact the development of healthy coping mechanisms. Children who experience trauma may not have access to healthy strategies for dealing with stress, such as support from caregivers or developing problem-solving skills. As a result, they may turn to maladaptive behaviors, including substance abuse, to cope with their emotions and navigate difficult situations. Substance abuse can provide a temporary escape from the pain and distress associated with trauma, reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
Breaking the Cycle
Understanding the relationship between childhood trauma and addiction is important for effective treatment and prevention strategies. It is essential to provide trauma-informed care that addresses both the addiction and the underlying trauma. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), trauma-focused therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) can effectively address both the trauma and the addiction simultaneously. Professional intervention and faith healing can be highly beneficial as well because they effectively manage the root cause of the issue.
It is crucial to prioritize trauma-informed care and ensure that comprehensive treatment approaches are in place to address the complex needs of those who have experienced childhood trauma and addiction.
Don’t hesitate if you or someone close to you is grappling with addiction. Take the first step towards achieving long-lasting recovery by contacting Christian’s Drug Rehab immediately. Our empathetic team of professionals is available to offer guidance throughout your journey toward healing and restoration. Get in touch with us to explore our customized treatment programs.












